|
|
Security Testing for E-Commerce Applications It seems that everyone is creating e-commerce applications these days with security being one of the greatest issues. The role of assessing security often falls to the tester, who may feel ill-prepared for the demands imposed by this new paradigm. Learn how to conduct a security assessment for e-commerce and what to look for.
|
Jonathan Beskin, Reliable Software Technologies
|
|
|
Exploiting a Broken Design Process A major flaw in the way most code is designed allows you to break the code by exploiting the flaw. Learn how this "trick" can force software into a state from which it produces incorrect results. Observe live demonstrations on applying this "trick" to popular software programs and code. Discuss ways to build test automation that methodically searches for these flaws.
|
James Whittaker, Florida Tech, Computer Science
|
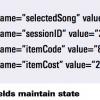 |
Hidden Risks in Web Code A look at the HTML source code behind Web sites can often reveal security issues that would never be uncovered by those blissfully ignorant of the code. This bug report will examine two common methods of maintaining state and passing data in Web-based systems–hidden form fields and the HTTP GET method–and demonstrate some of the associated security risks through an examination of HTML code.
|
|
|
|
STAREAST 2002: Testing Web Site Security The Internet can be a less-than-secure place to conduct business. So how do you make sure your Web site is secure from attack? Is a firewall the only line of defense you need? This presentation provides insight into the different attack points that a hacker could seek to exploit. It teaches you what to look for when testing the security of a Web site and delivers a simple, ten-step process for testing the security of a Web site.
|
Steve Splaine, Splaine & Associates
|
|
|
Behind Closed Doors: What Every Tester Should Know About Web Privacy The explosion of personal information on the Web has made privacy a primary concern. Here are pointers on making sure your site works for security-conscious users, as well as information to help you avoid inadvertent compromises of privacy.
|
|
|
|
Requirements Are Requirements Are Requirements - Not! "This isn't what I need," states Customer Bob. "But it's what you said you wanted," replies Engineer Joe. "It's not right. I need something else." We've all encountered this classic users-don't-know-what-they-want scenario. The fact that software professionals continue to have this same experience over and over again suggests that we're overlooking the real reasons for the user/engineer disconnect. This presentation contrasts the different uses of the term "requirements" as it explores the possible solutions to improving understanding between business people and technical people.
|
Robin Goldsmith, GoPro Management, Inc.
|
|
|
Get Real! Creating Realistic, Actionable Project Schedules The preparation of a realistic, practical project schedule is an essential management function for obtaining stakeholder commitment, setting expectations, and communicating within the team and organization what is achievable. Doing this preparation well is another challenge-one that must be conquered. Rex Black helps participants see the bigger project scheduling picture by focusing on issues such as constituent tasks, the underlying dependencies between them, and the risks attached to the completion of those tasks.
|
Rex Black, Rex Black Consulting Services, Inc.
|
|
|
Bottlenecks Exposed: The Most Frequently Found Performance Problems Dan Downing's experience with stress testing projects has revealed a handful of common denominators present in most Web site performance problems. These include memory starvation; a CPU-gobbling database access; improperly sized heaps, caches, and pools; poor application design; and load balancing that doesn't balance. This presentation uses actual B2C and B2B project examples to show you a symptom-measurement-diagnostic approach to understanding, exposing, and documenting these common problems.
|
Dan Downing, Mentora
|
|
|
Targeted Software Fault Insertion Since the completely random software fault insertion techniques suggested in much of the research literature are not practical for most software products, this paper suggests that a modest targeted software fault insertion effort for a few common error conditions can have a dramatic impact on defect detection rates and quality. The paper uses the example of a software fault insertion subsystem, codenamed Faulty Towers, which was added to Mangosoft Incorporated’s test automation in order to target
common failures and errors.
|
Paul Houlihan, MangoSoft Corporation
|
|
|
Predictive Metrics to Estimate Post Project Costs How much will it cost to support your software project based on current estimations? Discover the answer to this question by using statistical estimation methods-including the S-curve and the Rayleigh curve-to help you determine where your projects are in relation to required quality and trendings to meet your post-project cost goals. Learn how to use metrics to predict post-project costs and make better release decisions based on these predictions.
|
Geoffrey Facer, Intel Corporation
|

